What is an Earnings Surprise?
Casual investors need to know what an earnings surprise is, and how it may affect their investment decisions.
How are earnings announced?
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires companies to publish their unaudited financial results in quarterly statements (called a 10-Q) no later than 35-45 days after the end of each quarter, and an annual 10-K statement at the end of the financial year. Larger companies tend to present their quarterly results via publicly accessible conference call and the web, along with other relevant information (profit and loss, operating expenses, issues that affected earnings, future plans, etc.).
Firms may submit a non-timely (NT) filing if results must be postponed. The NT filing gives firms an additional five days to submit. Financial analysts typically consider an NT filing to be an indicator of trouble for the firm, and lower expectations, and projections of stock price, as a result.
What is a Form 10-Q or Form 10-K?
Form 10-Q requires the following four items:
- Financial statements, including balance sheet, income statement, cash flows, and earnings per share.
- Analysis by management of the firm’s liquidity, resources, operations, financial condition, and changes during the quarter
- Market conditions, including the impact on revenue of forces outside company control, including inflation, environment, regulations, and competition.
- Disclosure of management controls to protect firm assets and ensure accuracy of reporting.
Additionally, firms must disclose additional information that could potentially impact future earnings:
- Events related to legal proceedings that occurred during the quarter.
- Risk factors, which can very broadly include global economic conditions, unanticipated change in the market, product transitions, availability of raw materials, etc.
- Unregistered stock sales, including stock repurchases.
- Defaults on principal or interest on company debt
- Mine safety disclosures
- Other information, a catch-all where changes in senior management and other information may be mentioned.
- Exhibits, which lists the filing date, form identifier, and description of forms required by the SEC during the quarter.
Revenue and expense costs are broken down on the form, and show the following:
- Net sales
- Cost of sales (marketing, etc.)
- Margin (net sales – cost)
- Operating expenses (research and development, administrative costs)
- Operating income
- Taxes
- Earnings per share
- Shares outstanding (basic and diluted)
For comparison, the form includes revenue and costs for the same quarter from the prior year.
When are earnings announced?
Firms can choose any day to publish or announce their quarterly earnings within the reporting period mandated by the SEC.
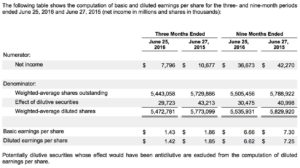
How are earnings per share calculated?
Earnings per share are computed by dividing income by the average number of common stock outstanding during the quarter, which is referred to as basic shares outstanding, since it excludes shares held by the firm for employee incentives, stock purchase plans, etc.
- The formula for calculating earnings per basic share is net income / basic shares
Earnings per diluted shares are computed by dividing income by the average number of common stock outstanding during the quarter, plus additional shares purchased under the firm’s stock purchase plan, unvested restricted stock, and stock options.
- The formula to calculate earnings per diluted share is net income / diluted shares
What is an earnings consensus?
An earnings consensus is the average of quarterly earnings predictions from leading financial analysts, in advance of a company’s announcement.
- Leading up to the announcement, financial analysts try to predict earnings results. Analysts estimate upcoming earnings results by considering the following:
- Trends in the stock price
- Conditions of the market into which the company sells
- Supplier information (for example, suppliers providing detailed sales of specific components can indicate the sales of a company’s product that depends on those components)
- Results of market competitors
- Guidance provided at the previous announcements call by the company itself
- Conditions outside the company’s control, including inflation, available credit, and other information
While analysts have have access to a common set of data, each may weight aspects of the data with specialized analytical models, leading to different estimates. The average earnings estimate of leading analysts is averaged into a consensus estimate. An earnings announcement that is outside the consensus estimate, either higher or lower, is considered an earnings surprise. These surprises typically have a short term effect on the stock price.
What is an earnings surprise?
An earnings announcement becomes and earnings surprise when the actual earnings per share differ from the pre-announcement earnings (EPS) consensus, and are above or below analysts’ expectations.
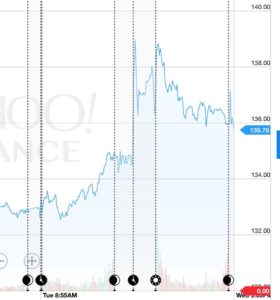
An earnings surprise can have a short term positive or negative effect on stock price. If the actual EPS reflects a loss, but is not as bad as the consensus estimate forecast, the price of the company’s stock may go up. This is because the consensus EPS is usually already accounted for in the stock price. For instance, based on guidance, market conditions, and competitors performance, analysts’ recent EPS consensus for Boeing (BA) was -$0.88 per share, a net loss; the expected loss was already accounted for in the price of the stock. Boeing’s actual EPS was -$0.44 per share, so 50% better than expected. The immediate result was an 8% increase in the stock price.
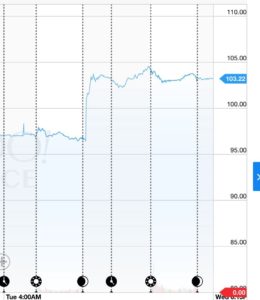
In the case of Apple (AAPL), the EPS consensus expected a lower profit than the same quarter last year, and its stock price reflected this low expectation. The EPS consensus was $1.39 per share, 2.16% lower than the actual EPS of $1.42. Despite this quarter’s EPS was lower than a year ago, the EPS consensus had been built already been built into the price. Apple’s stock price shot up over 7% on the news.
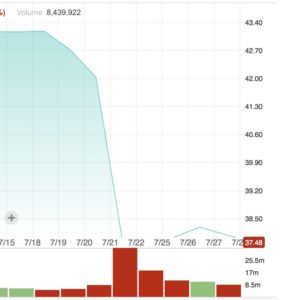
Stock Price for Southwest Airlines (LUV)
Actual EPS losses that are worse than projected, even by a relatively small percentage, can have a disastrous effect on a company’s stock price in the short term. The consensus EPS for Southwests Airlines (LUV) was $1.22, so when the firm announced an actual profit of $1.19 per share, the -2.46% difference caused the stock price to plummet nearly 16%.
In nearly every case, an earnings surprise causes trading volume to spike during the days following the 10-Q announcement, so the opportunity to take advantage of the change in stock price is limited to the first hour or so of the first day’s trading.